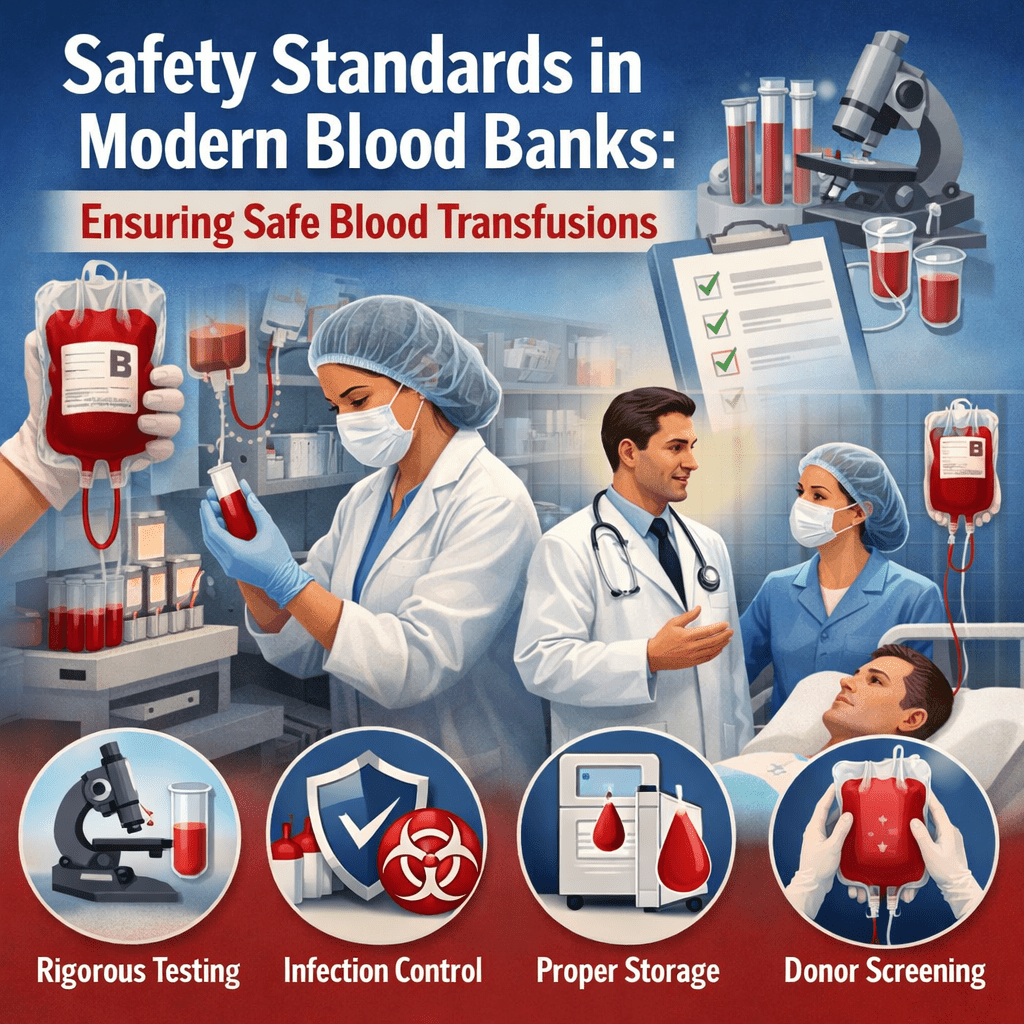
Blood banks play a critical role in healthcare systems by ensuring the availability of safe and life-saving blood for patients in need. Because blood transfusion involves direct transfer into the human body, maintaining strict safety standards is essential. Modern blood banks follow internationally recognized protocols and advanced technologies to ensure that every unit of blood is safe, hygienic, and traceable.
Donor Eligibility and Screening
Safety begins with careful donor selection. Before donating blood, every donor is required to complete a detailed health questionnaire. This helps identify any medical conditions, recent illnesses, medications, travel history, or lifestyle factors that may pose a risk.
Trained medical staff also conduct a brief physical examination to check vital signs such as blood pressure, hemoglobin level, weight, and pulse. Only donors who meet established eligibility criteria are allowed to donate, reducing the risk of transmitting infections or complications.
Sterile and Hygienic Collection Process
Modern blood banks follow strict hygiene protocols during blood collection. Single-use, sterile needles and blood bags are used for each donor to prevent cross-contamination. These disposable materials are safely discarded after use, ensuring zero reuse.
Donation areas are cleaned and disinfected regularly, and staff members wear gloves and protective equipment throughout the process. These practices minimize the risk of infections for both donors and healthcare workers.
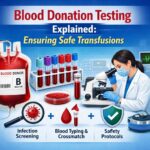
Mandatory Blood Testing
Every donated unit of blood undergoes mandatory laboratory testing before it can be used for transfusion. Blood banks screen for infectious diseases such as HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, syphilis, and malaria, following national and international guidelines.
Advanced testing methods, including automated analyzers and sensitive screening techniques, help detect infections even in early stages. Blood that does not meet safety standards is immediately discarded and never enters the supply chain.
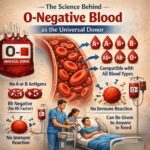
Blood Grouping and Compatibility Checks
Accurate blood typing is another essential safety standard. Blood banks determine the ABO blood group and Rh factor for every donation. Before transfusion, compatibility testing (cross-matching) is performed to ensure that the donor’s blood matches the recipient’s blood type.
This step helps prevent transfusion reactions, which can be life-threatening if incompatible blood is administered.
Proper Storage and Temperature Control
Blood components must be stored under strict temperature-controlled conditions to maintain their quality and effectiveness. Whole blood and red blood cells are stored in specialized refrigerators, platelets in temperature-controlled agitators, and plasma in deep freezers.
Modern blood banks continuously monitor storage temperatures using automated systems and alarms. Any deviation is immediately addressed to prevent spoilage or loss of blood units.
Traceability and Documentation
One of the most important safety measures is complete traceability. Each blood unit is labeled with a unique identification number that allows tracking from donor to recipient. This system ensures accountability and enables quick action in case of recalls or investigations. porn leaks Lexy
Detailed records are maintained for donor details, testing results, storage conditions, and transfusion history, ensuring transparency and compliance with regulatory standards.
Trained Staff and Regular Audits
Modern blood banks employ trained professionals, including pathologists, lab technicians, and nurses who follow standard operating procedures at every step. Regular training programs help staff stay updated on the latest safety guidelines and technologies.
In addition, blood banks undergo periodic inspections and audits by regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with safety regulations. These audits help maintain high standards and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Safety is the foundation of modern blood banking. Through strict donor screening, advanced testing, sterile procedures, proper storage, and robust documentation systems, blood banks ensure that every unit of blood is safe for patients. These standards not only protect recipients but also build public trust, encouraging more people to donate blood and contribute to saving lives.