Blood donation is a lifesaving act, but not everyone who comes forward is always eligible to donate. Blood banks follow strict medical guidelines to ensure the safety of both the donor and the recipient. Being rejected does not mean someone is unhealthy or permanently unfit to donate. In most cases, the rejection is temporary. sydney sweeney nudes
Below are the most common reasons why someone may be rejected from donating blood.
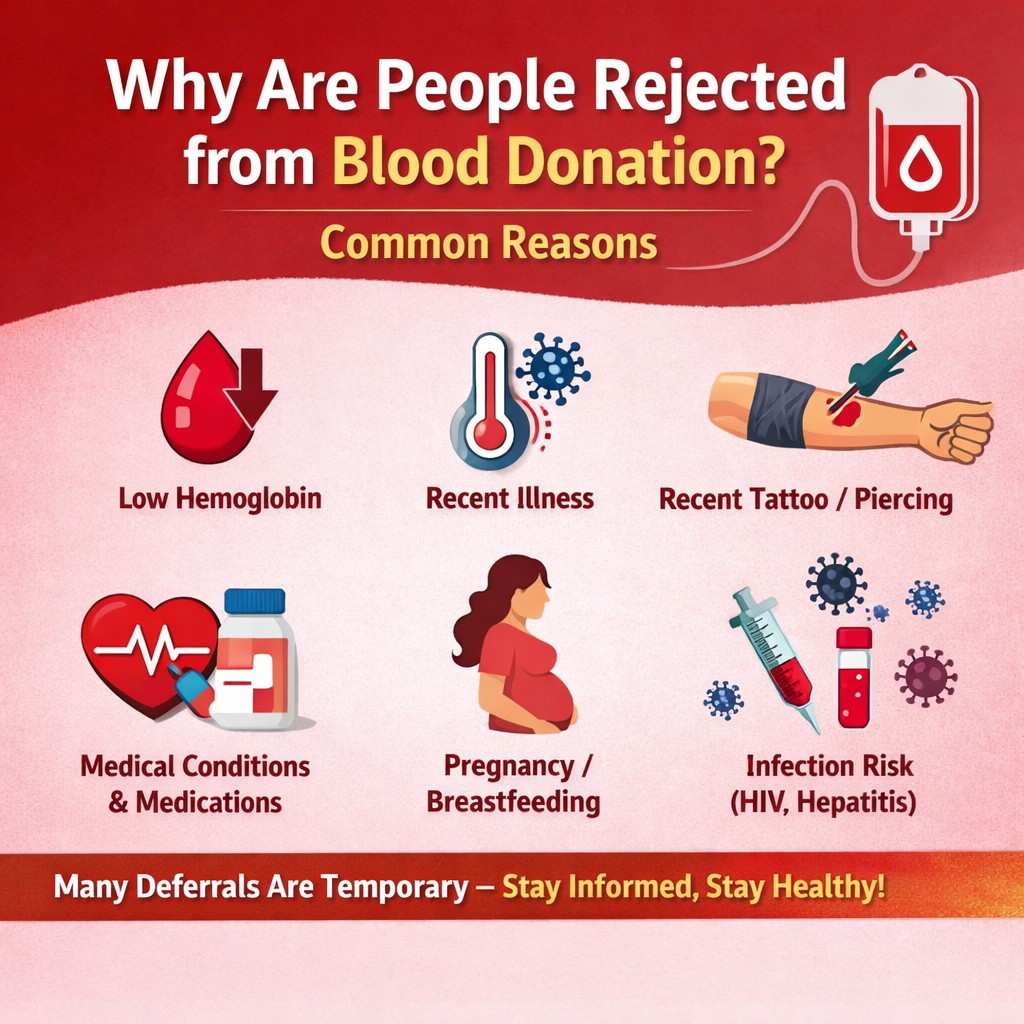
1. Low Hemoglobin (Anemia)
One of the most common reasons for rejection is low hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin carries oxygen in the blood, and donating with low levels can make the donor weak or dizzy.
-
Minimum required level is usually 12.5 g/dL
-
More common in women due to iron deficiency
Usually temporary; iron-rich diet or supplements help.
2. Low or High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure must be within a safe range to donate.
-
Too low BP may cause fainting
-
Too high BP increases health risks
Often temporary and manageable with medical advice.
3. Low Body Weight
Most blood banks require a minimum weight of 45–50 kg.
-
Lower weight increases risk of weakness after donation
Temporary; eligibility improves with healthy weight gain.
4. Recent Illness or Infection
If a person has had:
-
Fever
-
Cold or flu
-
Diarrhea
-
COVID-19 or other infections
They may be deferred to prevent infection transmission.
Usually temporary until full recovery.
5. Recent Surgery or Medical Procedures
Recent surgeries, dental procedures, or major treatments may require a waiting period.
-
Minor procedures: short deferral
-
Major surgeries: longer deferral
Temporary; donation allowed after recovery.
6. Recent Vaccination
Some vaccinations require a waiting period before donating blood.
-
Live vaccines often need longer deferral
-
Inactivated vaccines may need only a few days
Temporary and precautionary.
7. Chronic Medical Conditions
Some long-term health conditions may lead to rejection, such as:
-
Heart disease
-
Epilepsy
-
Certain cancers
-
Severe asthma
Can be temporary or permanent depending on condition.
8. Diabetes (in Some Cases)
People with diabetes may be deferred if:
-
Blood sugar is uncontrolled
-
On certain insulin regimens
Well-controlled diabetes may still allow donation.
9. Recent Tattoo or Piercing
Tattoos or piercings done recently can increase the risk of bloodborne infections.
-
Waiting period is usually 3–12 months
Temporary deferral.
10. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnant women and those who recently delivered are deferred to protect their health.
-
Donation allowed after a safe recovery period
Temporary and health-related.
11. Risk of Bloodborne Infections
Individuals at higher risk of infections like:
-
HIV
-
Hepatitis B or C
May be permanently deferred to ensure recipient safety.
Permanent in some cases.
12. Alcohol or Medication Intake
-
Alcohol intake within 24 hours
-
Certain medications like antibiotics or blood thinners
Usually temporary.
Important Things to Remember
-
Rejection does not mean permanent disqualification
-
Many deferrals are short-term
-
Always be honest during screening
-
Follow medical advice to become eligible in the future
Final Thoughts
Blood donation guidelines exist to protect lives. If you are rejected once, don’t be discouraged. Take care of your health, follow recommendations, and try again. Your willingness to donate already makes a difference.